Citation
Bryan B. Bozeman, Paul G. Matson, Christopher R. Derolph and Scott T. DeNeale. 2025. HydroBio: Hydropower Capacity and Freshwater Biodiversity in Conterminous United States Sub-basins. HydroSource. Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Oak Ridge, Tennessee, USA. DOI: 10.21951/HydroBio/2569066
Overview
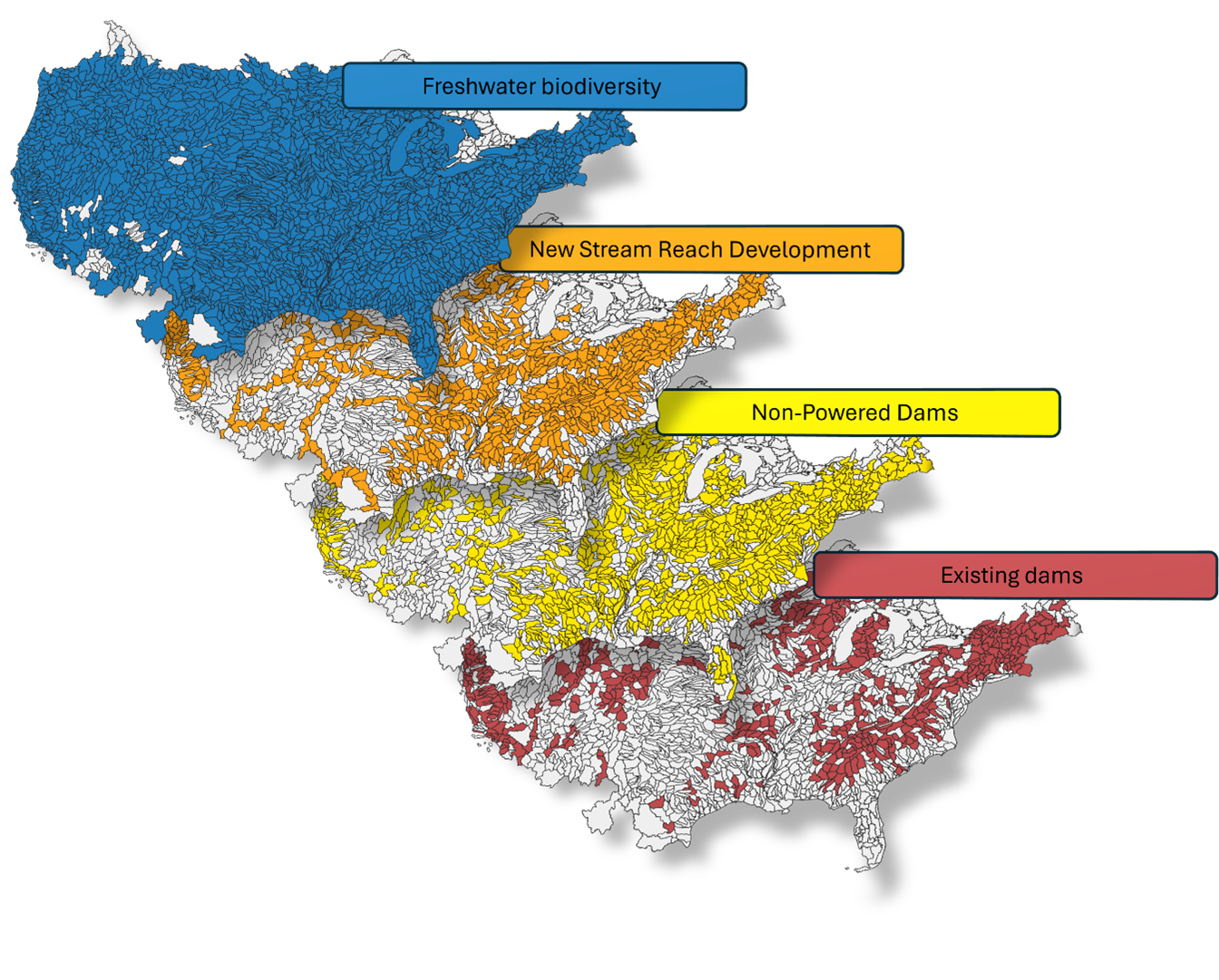
This dataset summarizes existing and potential hydropower capacity and freshwater biodiversity at the sub-basin level throughout the conterminous United States (CONUS). It contains descriptive information regarding each sub-basin (e.g., 8-digit hydrologic unit code identifier, name, states, and size) along with sub-basin-level summaries of: 1) existing hydropower capacity (MW), 2) potential nominal non-powered dam (NPD) capacity (MW), 3) potential capacity of new stream reach development (NSD) (MW), and 4) freshwater biodiversity, including the total richness of fish, crayfish, and mussels and metrics that account for how rare and threatened those species tend to be. Hydropower data were obtained from Oak Ridge National Laboratory data resources (Existing Hydropower Assets, Non-Powered Dam Technical Potential, and New Stream Reach Development). Freshwater biodiversity data were obtained from NatureServe. Sub-basin characteristic information was obtained from the United States Geological Survey. Additionally, long data that provide lists of unique elements within each sub-basin for each constituent data resource (e.g., NatureServe, Existing Hydropower Assets) are provided to enhance dataset utility for users. The dataset provides, for the first time, a national-level assessment of existing and potential hydropower capacity in the context of freshwater biodiversity and is a valuable resource for stakeholders tasked with providing affordable, reliable energy to the American public while maintaining or enhancing invaluable freshwater resources. The dataset contains six data files in comma separated (*.csv) format that are within a zipped file.
The HydroBio Dataset was produced through federal funding from the US Department of Energy’s Water Power Technologies Office as a part of the Standard Modular Hydropower (SMH) Technology Acceleration project. The SMH project promotes standardization, modularity, and environmental compatibility as three enabling principles of a low-cost, environmentally compatible hydropower growth strategy. Through research and development efforts focused on applications of hydropower to new stream reach development and non-powered dam retrofits, ORNL emphasized the importance of balancing power production and the related technical and economic objectives with environmental objectives, including maintaining environmental conditions, such as biodiversity. The HydroBio Dataset reflects this multi-purpose strategy for balancing social demands with environmental stewardship and enables decision-making through application of two key parameters affecting water resource management.
Methodology:
The HydroBio Dataset combines ORNL data products and NatureServe freshwater fish, mussel, and crayfish distribution data to summarize existing and potential hydropower capacity and freshwater biodiversity in every hydrologic sub-basin (8-digit hydrologic unit code) in the conterminous United States (CONUS). The complete methodology of dataset assembly is reported in the companion manuscript to this dataset. Briefly, CONUS sub-basins were delineated using the USGS Watershed Boundary Dataset (WBD; U.S. Geological Survey, 2024). Existing and potential hydropower capacity in each sub-basin were characterized where there were active hydropower plants, non-powered dams (NPD), or new stream reach development (NSD) watersheds using ORNL’s Existing Hydropower Assets database (EHA; Johnson et al., 2023), NPD Technical Potential dataset (Hansen et al., 2024), and New Stream-reach Development dataset (Kao et al., 2014), respectively. These characterizations include the total number of each entity (e.g., existing dams or new stream reaches) per sub-basin as well as the actual or potential total and mean capacity and total and mean average annual generation.
Freshwater biodiversity per CONUS sub-basin was characterized using NatureServe’s freshwater species distribution data dataset (NatureServe, 2020; https://explorer.natureserve.org/), the International Union for Conservation of Nature Red List of Threatened Species (IUCN, 2024; https://www.iucnredlist.org/), and the North American Freshwater Migratory Fish Database (NAFMFD; Dean et al., 2022). These resources allowed calculations of the total number of fish, crayfish, and mussel species present in each sub-basin (along with total richness of all freshwater species) and additional biodiversity metrics that account for the rarity and threat level of each species in each sub-basin. These data summaries were combined to create a data resource that consists of six distinct comma separated (*.csv) data files. The primary HydroBio Dataset contains 48 variables describing sub-basin characteristics, potential and actual hydropower capacity, and freshwater biodiversity per 2,193 sub-basins in CONUS. The long data associated with each constituent dataset (existing hydropower capacity, non-powered dam potential, new stream reach development potential, and biodiversity) is also provided so that Users can further explore specific dynamics within sub-basins (e.g., distinct non-powered dams or species per sub-basin). The variables provided in the HydroBio Dataset and supporting long data files are defined and described in the data dictionary data file. The HydroBio Dataset and accompanying data resources will support the hydropower community in understanding how actual and potential hydropower capacity are distributed relative to freshwater biota and potentially help inform decisions about how best to continue to provide clean, reliable energy to the American public while maintaining or enhancing America’s freshwater ecosystems.
Science Themes
Related Records
Existing Hydropower Assets (EHA) Plant Database, 2024
The Existing Hydropower Assets (EHA) Plant Database is a geospatially comprehensive point-level dataset containing locations and key characteristics of U.S. hydropower plants that are currently operational.
View DatasetHydropower Potential from New Stream-Reach Development for the Conterminous United States
This dataset is a summary of hydropower potential data (high-energy intensity stream-reaches and new potential areas for hydropower development) and environmental attributes aggregated to HUC10 watersheds for the Conterminous United States.
View DatasetHydroFish: Freshwater Fish Co-occurrence with Hydropower Plants and Non-Powered Dams in Conterminous United States Sub-basins
The HydroFish dataset lists all existing hydropower plants (EHA) and non-powered dams (≥ 0.001 MW potential nominal capacity), delineates the hydrologic sub-basins in which they are situated, and then lists all freshwater fish species reported to occur in those sub-basins.
View DatasetNational Hydropower Fish Passage Database
This database contains information on fish passage facility engineering characteristics, targeted fish species, operational schedule, and costs, which is of great value to a diverse range of stakeholders.
View Dataset